Frequently Asked
Questions (FAQs)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which is highly contagious and spreads through direct contact with an infected person's rash or through the air via coughing or sneezing.
The symptoms of Chickenpox include a rash that typically starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body, along with fever, fatigue, and itching.
The best way to prevent Chickenpox is to get vaccinated. Practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and avoiding contact with people who are sick, can also help reduce your risk of contracting the virus.
Yes, adults can get Chickenpox if they have not had it before or have not been vaccinated against it.
Yes, there is a safe and effective vaccine for Chickenpox. It is recommended for all children and adults who have not been infected before Chickenpox or the vaccine yet.
Yes, the Chickenpox vaccine is generally considered safe and effective. However, vaccines containing gelatin can cause anaphylactic shock and autoimmune disorders. Nexipox is the only Chickenpox vaccine that does not contain any harmful agents like gelatin and MSG, which makes Nexipox the safest Chickenpox vaccine for both children and adults.
The Chickenpox vaccine is highly effective. It reduces the risk of getting Chickenpox by about 90% and the risk of severe Chickenpox by about 95%.
While it's rare to get Chickenpox more than once, it is possible for the virus to reactivate later in life and cause a condition called shingles.
While Chickenpox is usually a mild illness, it can be dangerous in certain groups of people, including newborns, pregnant women, adults, and people with weakened immune systems. Potential complications include bacterial infections, pneumonia, encephalitis, and more.
Yes, Chickenpox is highly contagious and can be spread from person to person through direct contact or respiratory secretions. A person with Chickenpox is contagious from 1-2 days before the rash appears until all the blisters have crusted over.
The Chickenpox vaccine is not recommended for pregnant women. Women who are planning to become pregnant should wait at least one month after receiving the vaccine before trying to conceive.
The protection from the Chickenpox vaccine can last for many years, and some studies suggest that it may provide lifelong immunity.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that children receive two doses of the Chickenpox vaccine, with the first dose given at 12-15 months of age and the second dose given at 4-6 years of age. Adults who have not had Chickenpox or the vaccine should also consider getting vaccinated.
Chickenpox is typically diagnosed based on the characteristic rash and symptoms. A blood test or viral culture may be performed in some cases.
Chickenpox is usually treated with over-the-counter medications to reduce fever and itching. Antiviral medications may be prescribed in some cases, especially for people with weakened immune systems or at higher risk of complications. Consult your doctor.
Chickenpox usually lasts about 7-10 days, with new blisters forming for the first few days and then scabbing over and healing. The rash and other symptoms typically go away within-3 weeks.
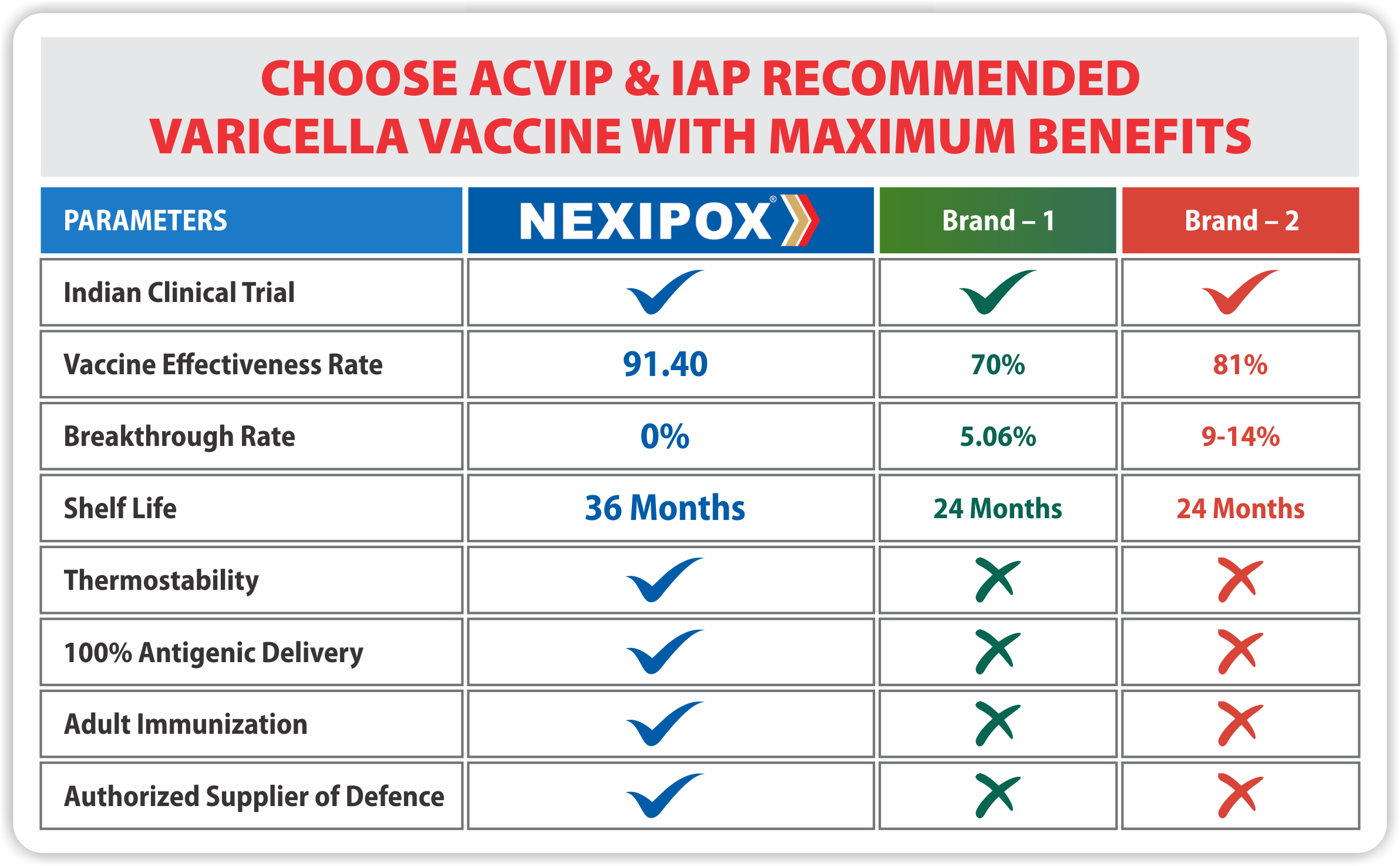
It is always advisable to consult your healthcare provider/Doctor before carrying out vaccination/ since they are the best judge. However there are some features which are important in vaccines.
- Vaccine Effectiveness: It’s an important parameter to know how vaccines work in natural environment.
- Safety: safety of a vaccine is very important. Do check what stabilizer is being used in it since some stabilizer like Gelatin can causes anaphylaxis in some cases (add this ref link: Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 53, 189-195, 2000).
- Breakthrough Rate: It’s important to know whether vaccine causes contraction of varicella infection after administration. Hence it is better to check the breakthrough rate of the vaccines if available.
- Stability: As vaccines need to be stored at a particular temperature in cold chain, so stability plays an important role in providing efficacy & potency. One known stabilizer used in vaccines is Trehalose; which provides greater thermostability to the vaccines, and thus can provide better efficacy.
We don’t recommend self vaccination, always consult your doctor